lms-esp32-pybricks-info
Using a VL53L0X TOF (laser distance) sensor with the LMS-ESP32 board from Antons Mindstorms and LEGO® Spike running Pybricks
If you only want to connect a single VL53L0X and expose it as a LEGO compatible sensor, follow Antons article.
This document explains how to expose them with the PUPRemote framework and compares with the LEGO ultrasonic sensor.
Mounting
Use a 3D printed case, countersunk M3 screws that fit nicely to the liftarm holes, ..., or simply zip ties:

Latency
A LEGO ultrasonic sensor is directly attached to the LEGO Spike, but for the TOF sensor the data goes over one aditional hop (the LMS-ESP32) so it has a higher latency. By using channel instead of command, this can be minimized.
command Variant
Simple code, but low sample rate and high latency.
The call blocks until the measurement is ready. See code at the end.
As already mentioned in Anton's article, the VL35L0X by default needs approximately 30 milliseconds for a measurement, so you have to use rh.call('tof', wait_ms=30), resulting in a round trip time of over 40 milliseconds.
channel Variant
Best sample rate, lowest latency.
After the first call, channels are always non-blocking, unless you interleave with other command or other channel calls.
Values are calculated in the background and send to the Spike when a new value is available. The rh.call('tof') returns in less than a millisecond with the latest received value.
Requires >= MicroPython v1.25.0 firmware.
Measurement Duration
The LEGO ultrasonic sensor returns a new value each 20 msec.
The VL32L0X has a configurable measurement duration, with 30 msec default and 20 msec minimum.
Accuracy
The VL53L0X has limited accuracy and a high jitter. Check here and here for discussion and correction strategies.
The measured values are not exact and surprisingly depend on the color of the reflected object, e.g.
| Wall proximity | LEGO ultrasonic sensor | VL32L0x with white wall | VL32L0X with brown wall | VL32L0X with black wall |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mm | 50 mm | 55 mm | 51 mm | 37 mm |
| 100 mm | 100 mm | 108 mm | 106 mm | 74 mm |
| 150 mm | 150 mm | 166 mm | 163 mm | 125 mm |
| 200 mm | 200 mm | 218 mm | 213 mm | 180 mm |
The LEGO ultrasonic sensor has basically no jitter. Depending on the measurement duration the VL32L0X values have a significant jitter, e.g.
| Measurement time | Jitter |
|---|---|
| 20 msec | +-6 mm |
| 30 msec | +-4 mm |
| 200 msec | +-1.5mm |
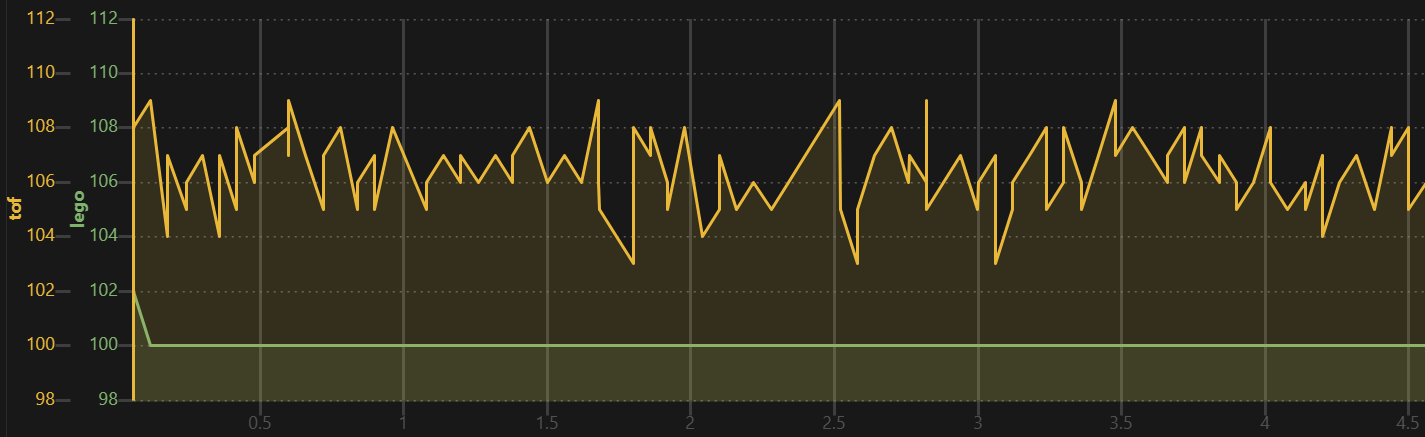
The limited accuracy was reproducible when attached to an Arduino.
Libraries
I started with the https://github.com/antonvh/PUPRemote/blob/main/examples/emulate_dist_sensor/VL53L0X.py module, which is identical to uceeatz/VL53L0X with replaced Timer module.
the set_measurement_timing_budget(budget_us) function is not working correctly. The budget_us value is not the total measurement time in microseconds. I found these working values:
| Value | Measurement time |
|---|---|
| 226 000 | 20 msec |
| 227 000 | 30 msec (default) |
| 228 000 | 50 msec |
| 229 000 | 160 msec |
| 230 000 | 320 msec |
| 231 000 | 625 msec |
The antirez/vl53l0x-nb module has a correctly working measurement_timing_budget property.
Both libraries report slightly different distances. Unclear which is better.
Sensor Comparison
Unclear if the jitter is a real issue. To be verified with a PID based wall follower.
Correcting the values with a linear function is possible but not perfect as the errors also look non-linear.
The VL53L0X data lags approximately 20msec behind the LEGO ultrasonic sensor data. Should be sufficient.
The VL53L0X has a narrower field of view. In the diagram below it is slightly smaller than the passed brick, and for the LEGO ultrasonic sensor it is slightly larger than the brick. Both look ok-ish.
The Diagrams shows the channel variant, driving with brisk 200 mm/sec alongside a wall and passing a 4 by 6 brick. Every measurement looks different. The first is an example with 20msec measurement duration, the second with 30ms.
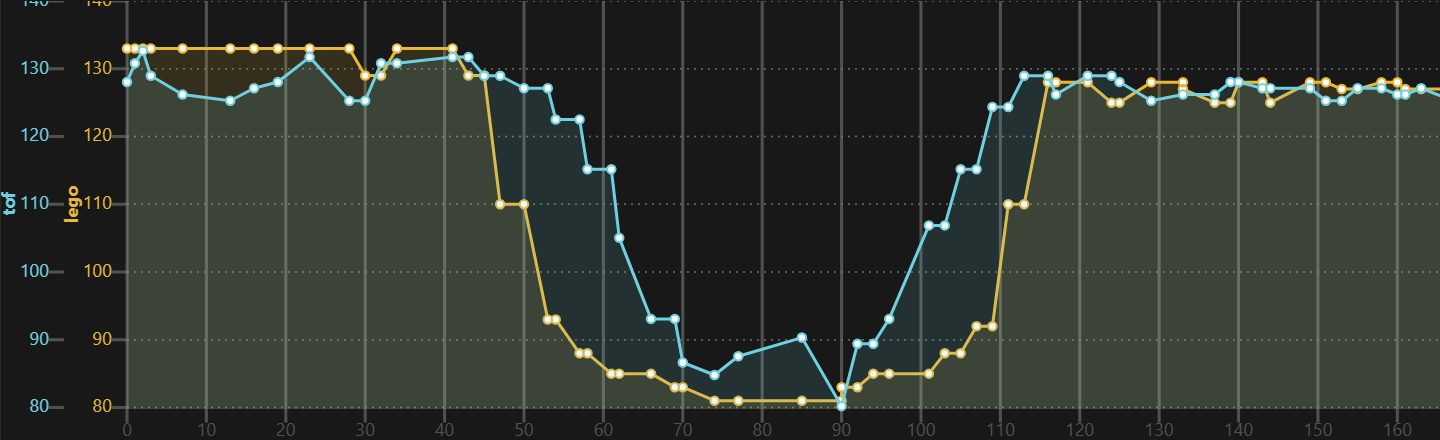
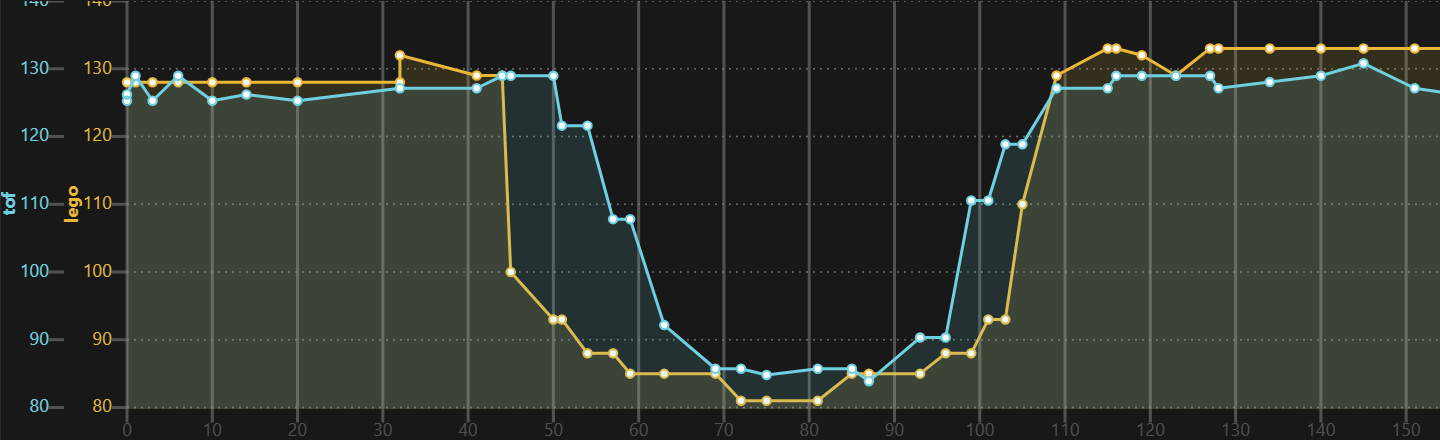
Code
LMS-ESP32 code:
Add a file named VL53L0X.py with content from https://github.com/antonvh/PUPRemote/blob/main/examples/emulate_dist_sensor/VL53L0X.py
Command variant
from machine import SoftI2C, Pin
from pupremote import PUPRemoteSensor
from VL53L0X import VL53L0X # https://github.com/antonvh/PUPRemote/blob/main/examples/emulate_dist_sensor/VL53L0X.py
vl53l0x = VL53L0X(SoftI2C(scl=Pin(4), sda=Pin(5), freq=200000))
def tof():
return vl53l0x.read()
rs = PUPRemoteSensor(power=True)
rs.add_command('tof', 'H', '')
while True:
rs.process()
Channel variant
from machine import SoftI2C, Pin
from pupremote import PUPRemoteSensor
from VL53L0X import VL53L0X # https://github.com/antonvh/PUPRemote/blob/main/examples/emulate_dist_sensor/VL53L0X.py
vl53l0x = VL53L0X(SoftI2C(scl=Pin(4), sda=Pin(5), freq=200000))
vl53l0xOn = False
def tofOn(on):
global vl53l0xOn
vl53l0xOn = on
rs = PUPRemoteSensor(power=True)
rs.add_channel('tof', 'H')
rs.add_command('tofOn', '', 'B')
vl53l0x.start()
while True:
rs.process()
if vl53l0xOn:
rs.update_channel('tof', vl53l0x.read())
With vl53l0x.start() the library measures in continuous mode. Else the vl53l0x.read() command would start a new measurement and the sample rate would be 1-2msec lower as rs.process() waits some time for requests.
Using the other library will not block the main loop. This is prefered if your LMS-ESP32 also has to handle other sensors or actors.
Pybricks code:
from pybricks.pupdevices import UltrasonicSensor
from pybricks.parameters import Port
from pybricks.tools import StopWatch
from pupremote_hub import PUPRemoteHub # https://github.com/antonvh/PUPRemote/blob/main/src/pupremote_hub.py
sw = StopWatch()
us = UltrasonicSensor(Port.B)
rh = PUPRemoteHub(Port.A)
#rh.add_command('tof', 'H', '') # command variant
rh.add_channel('tof', 'H') # channel variant
rh.add_command('tofOn', '', 'B') # channel variant
print('time; lego; tof')
rh.call('tofOn', 1) # channel variant
while True:
a = us.distance()
#b = rh.call('tof', wait_ms=30) # command variant
b = rh.call('tof') # channel variant
b = b * 0.92 + 2 # correction for brown wall
print(f'{sw.time()}; {a}; {b}')